GEF Editor Tutorial
编辑器
GEF中三种默认的编辑器:
- org.eclipse.gef.ui.parts.GraphicalEditor:不带Palette。
- org.eclipse.gef.ui.parts.GraphicalEditorWithFlyoutPalette:带一个可以隐藏的Palette。
- org.eclipse.gef.ui.parts.GraphicalEditorWithPalette:带一个固定的Palette。
组件
- EditDomain:是一个工具集,它将CommandStack,GraphicalViewer以及Palette相关的内容整合到一起。它也用来调度Palette中的所有工具,以及根据不同的工具去调用不同的Command,然后在CommandStack中执行。
- EditPartViewer:
- 它是一个SWT Control的实现,所有的图形都创建在这个SWT Control上面。
- 它用来管理所有的EditPart的生命周期。
- 它也是一个SelectionProvider,会提供一组选中的EditPart,选中的所有的EditPart中,最后一个也被标记为Primary Selection。
- 和JFace中的Viewer类似,EditPartViewer也需要一个input来实现子元素的加载,它是通过setContents方法来实现的;contents可以是一个具体的模型,也可以是模型对应的EditPart,但前提是你必须先设置了对应的EditPartFactory。
- Root EditPart并不是指root模型对应的EditPart,这里的Root EditPart是通过一个专门的接口org.eclipse.gef.RootEditPart实现的,主要作用是实现一些不同的分层(Layer)。
- KeyHandler用来设置一些特殊的键盘事件绑定。
- EditPart和EditPartFactory:
- EditPartFactory是用来根据不同的模型创建EditPart的一个工厂类。
- 每一个EditPart都对应一种模型,它相当于模型的控制器(Controller)。
- 每一个EditPart都必须添加一个Figure或者TreeItem来作为视图(View)。
- 每一个EditPart中都会添加零到多个EditPolicy来实现编辑。
- EditPart中子元素的加载可以通过实现getModelChildren()来完成。
- EditPolicy:用来显示Feedback和返回各种工具或操作所对应的Command。
- CommandStack和Command:
- CommandStack是用来执行并记录当前Command信息的工具,同时它也是Undo和Redo操作的依赖。
- Command是所有编辑实现过程。
- Palette:工具条,包含选择,创建节点和创建连线等。
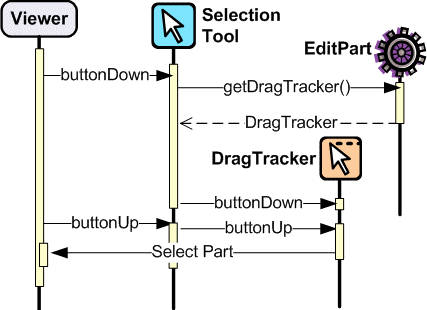
示例
创建一个GraphicalEditor的子类。
public class ShapesEditor extends GraphicalEditorWithFlyoutPalette { }设置EditDomain,通常使用org.eclipse.gef.DefaultEditDomain。
public ShapesEditor() { setEditDomain(new DefaultEditDomain(this)); }根据模型创建EditPart。
class DiagramEditPart extends AbstractGraphicalEditPart { protected void createEditPolicies() { // disallows the removal of this edit part from its parent installEditPolicy(EditPolicy.COMPONENT_ROLE, new RootComponentEditPolicy()); // handles constraint changes (e.g. moving and/or resizing) of model // elements // and creation of new model elements installEditPolicy(EditPolicy.LAYOUT_ROLE, new ShapesXYLayoutEditPolicy()); } protected IFigure createFigure() { Figure f = new FreeformLayer(); f.setBorder(new MarginBorder(3)); f.setLayoutManager(new FreeformLayout()); // Create the static router for the connection layer ConnectionLayer connLayer = (ConnectionLayer) getLayer (LayerConstants.CONNECTION_LAYER); connLayer.setConnectionRouter(new ShortestPathConnectionRouter(f)); return f; } protected List getModelChildren() { return getCastedModel().getChildren(); // return a list of shapes } }创建EditPartFactory并在EditPartViewer中调用。
public class ShapesEditPartFactory implements EditPartFactory { public EditPart createEditPart(EditPart context, Object modelElement) { // get EditPart for model element EditPart part = getPartForElement(modelElement); // store model element in EditPart part.setModel(modelElement); return part; } private EditPart getPartForElement(Object modelElement) { if (modelElement instanceof ShapesDiagram) { return new DiagramEditPart(); } if (modelElement instanceof Shape) { return new ShapeEditPart(); } if (modelElement instanceof Connection) { return new ConnectionEditPart(); } throw new RuntimeException("Can't create part for model element: " + ((modelElement != null) ? modelElement.getClass().getName() : "null")); } } //在编辑器中设置 GraphicalViewer viewer = getGraphicalViewer(); viewer.setEditPartFactory(new ShapesEditPartFactory());给EditPartViewer中设置Contents。
GraphicalViewer viewer = getGraphicalViewer(); viewer.setContents(getModel()); // set the contents of this editor
GEF Example
- 安装GEF Example插件。
- 新建Example,GEF Example Plug-ins。
- 运行。
参考资料
Back to Home 上一篇:GEF Tutorial 下一篇:GEF EditParts Tutorial